Unveiling the Cosmic Dance: A Comprehensive Guide to the Aurora Borealis
Related Articles: Unveiling the Cosmic Dance: A Comprehensive Guide to the Aurora Borealis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Cosmic Dance: A Comprehensive Guide to the Aurora Borealis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Cosmic Dance: A Comprehensive Guide to the Aurora Borealis

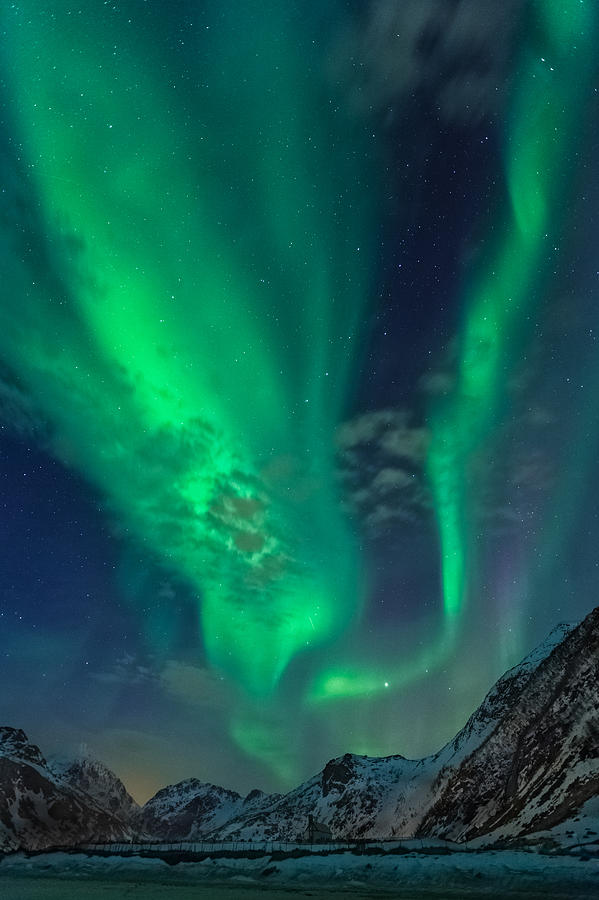
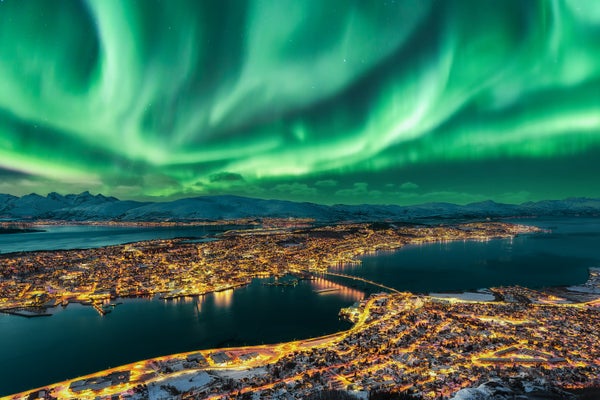
The Aurora Borealis, often referred to as the Northern Lights, is a mesmerizing celestial display that captivates audiences worldwide. This natural phenomenon, occurring in the Earth’s upper atmosphere, paints the night sky with vibrant hues of green, red, purple, and blue, creating a spectacle of ethereal beauty.
Understanding the Science Behind the Cosmic Canvas
The Aurora Borealis is a consequence of the interaction between charged particles from the sun, known as the solar wind, and the Earth’s magnetic field. This interaction triggers a chain of events that ultimately lead to the breathtaking display we witness.
-
Solar Wind: The sun continuously emits a stream of charged particles, primarily protons and electrons, known as the solar wind. This stream travels at speeds of hundreds of kilometers per second, carrying immense energy.
-
Earth’s Magnetic Field: The Earth possesses a protective magnetic field that acts as a shield against the harmful solar wind. This magnetic field extends far beyond the Earth’s atmosphere, forming a protective bubble known as the magnetosphere.
-
Interaction and Energy Transfer: When the solar wind encounters the Earth’s magnetic field, it gets deflected around the planet. However, some charged particles manage to penetrate the magnetosphere and become trapped in the Earth’s magnetic field lines.
-
Journey to the Atmosphere: These trapped particles are then guided by the magnetic field lines towards the Earth’s poles. As they descend towards the upper atmosphere, they collide with atoms and molecules in the thermosphere, primarily oxygen and nitrogen.
-
Excitation and Emission: These collisions cause the atoms and molecules to become excited, meaning they gain energy. As these excited particles return to their ground state, they release the excess energy in the form of light, creating the mesmerizing auroral displays.
The Colors of the Cosmic Show
The color of the Aurora Borealis depends on the type of gas atom or molecule that is excited and the energy level at which the particle is excited.
-
Green: The most common color of the Aurora Borealis, green is produced when oxygen atoms are excited at a lower energy level.
-
Red: Red auroras are rarer and occur when oxygen atoms are excited at a higher energy level. These displays typically appear at higher altitudes, above 150 kilometers.
-
Blue: Blue auroras are caused by nitrogen molecules being excited. They often appear at lower altitudes, below 100 kilometers.
-
Purple: Purple auroras are a combination of red and blue emissions, often seen in areas where the two colors overlap.
Beyond the Northern Lights: The Southern Hemisphere’s Counterpart
While the Aurora Borealis illuminates the skies of the northern hemisphere, its southern counterpart, known as the Aurora Australis, graces the skies above Antarctica and surrounding regions. The Aurora Australis shares the same scientific principles as its northern counterpart, with the only difference being its geographical location.
Factors Influencing the Intensity and Frequency of Auroral Displays
The intensity and frequency of auroral displays are influenced by several factors:
-
Solar Activity: The sun undergoes periods of increased activity, known as solar cycles, during which the solar wind becomes stronger and more intense. This leads to more frequent and vibrant auroral displays.
-
Geomagnetic Storms: Large disturbances in the Earth’s magnetic field, known as geomagnetic storms, can also trigger intense auroral displays. These storms are often caused by solar flares or coronal mass ejections, powerful bursts of energy from the sun.
-
Seasonality: Auroral displays are more frequent and intense during the winter months in both hemispheres. This is because the Earth’s magnetic field lines are more inclined towards the poles during these months, allowing more charged particles to penetrate the magnetosphere.
Exploring Related Searches: Expanding Your Knowledge
-
Best Places to See the Aurora Borealis: Understanding the best locations to witness the Aurora Borealis is crucial for any aspiring auroral enthusiast. Popular destinations include Alaska, Canada, Iceland, Norway, Greenland, Finland, and Russia. These locations offer optimal viewing conditions due to their proximity to the auroral oval, a ring-shaped region around the Earth’s magnetic poles where auroras are most frequent.
-
Aurora Borealis Forecast: Predicting auroral activity is an essential aspect of planning an auroral viewing trip. Websites and apps provide real-time forecasts based on solar activity and geomagnetic conditions, helping individuals choose the best time and location for viewing.
-
Aurora Borealis Photography: Capturing the ethereal beauty of the Aurora Borealis requires specific photographic techniques. These include using a tripod for stability, a wide-angle lens to capture the vastness of the sky, and a long exposure to allow sufficient light to enter the camera sensor.
-
Aurora Borealis Mythology: Throughout history, various cultures have developed myths and legends surrounding the Aurora Borealis. These stories often attributed the celestial display to supernatural beings or celestial events, reflecting the wonder and awe inspired by this natural phenomenon.
-
Aurora Borealis Research: Scientists actively study the Aurora Borealis to understand the processes governing the interaction between the solar wind and the Earth’s magnetic field. This research helps us better understand space weather, which can impact satellites, communication systems, and power grids.
-
Aurora Borealis Tours: Numerous tour operators offer guided tours specifically designed for viewing the Aurora Borealis. These tours provide expert guidance, comfortable accommodations, and transportation to optimal viewing locations.
-
Aurora Borealis Facts: Learning interesting facts about the Aurora Borealis can enhance the appreciation of this natural spectacle. For example, the Aurora Borealis can be seen from space, and its sound has been recorded, although it is typically inaudible to humans.
-
Aurora Borealis History: The Aurora Borealis has been observed and documented for centuries. Historical records reveal that ancient cultures around the world, from the Vikings to the Chinese, recognized and interpreted the Aurora Borealis in their own unique ways.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Aurora Borealis
-
What causes the Aurora Borealis?
The Aurora Borealis is caused by the interaction between charged particles from the sun, known as the solar wind, and the Earth’s magnetic field. -
Where can I see the Aurora Borealis?
The Aurora Borealis is primarily visible in the northern hemisphere, particularly in countries near the auroral oval, such as Alaska, Canada, Iceland, Norway, Greenland, Finland, and Russia. -
When is the best time to see the Aurora Borealis?
The best time to see the Aurora Borealis is during the winter months, from September to April, when the nights are long and dark. -
How often does the Aurora Borealis occur?
The frequency of auroral displays varies depending on solar activity. During periods of high solar activity, auroras can be seen more frequently. -
Can I hear the Aurora Borealis?
While the Aurora Borealis is primarily a visual phenomenon, some people claim to have heard crackling or hissing sounds associated with auroral displays. However, the scientific consensus is that these sounds are likely due to other factors, such as wind or ice. -
Is the Aurora Borealis dangerous?
The Aurora Borealis is a natural phenomenon that poses no danger to humans. -
What is the difference between the Aurora Borealis and the Aurora Australis?
The Aurora Borealis and the Aurora Australis are essentially the same phenomenon, occurring in the northern and southern hemispheres, respectively. -
How can I predict when the Aurora Borealis will occur?
You can predict auroral activity using websites and apps that provide real-time forecasts based on solar activity and geomagnetic conditions.
Tips for Witnessing the Aurora Borealis
-
Choose the Right Time: The best time to see the Aurora Borealis is during the winter months, from September to April, when the nights are long and dark.
-
Find a Dark Location: Light pollution can interfere with your ability to see the Aurora Borealis. Choose a location away from city lights and artificial illumination.
-
Check the Forecast: Websites and apps provide real-time forecasts based on solar activity and geomagnetic conditions.
-
Be Patient: The Aurora Borealis is a natural phenomenon, and its appearance can be unpredictable. Be patient and enjoy the anticipation.
-
Dress Warmly: Auroral viewing often takes place in cold climates, so dress warmly and in layers.
-
Bring a Camera: Capture the beauty of the Aurora Borealis with a camera. Use a tripod for stability, a wide-angle lens, and a long exposure.
-
Stay Safe: Always be aware of your surroundings and take precautions against the cold and darkness.
Conclusion
The Aurora Borealis is a testament to the awe-inspiring beauty and complexity of the natural world. This celestial spectacle, born from the interaction between the sun and Earth’s magnetic field, serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet and its place in the vastness of space. By understanding the science behind the Aurora Borealis, we gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders that lie beyond our atmosphere and the intricate processes that shape our universe. Whether witnessed from the frozen landscapes of the Arctic or the vastness of space, the Aurora Borealis continues to inspire wonder and awe in all who behold its ethereal dance.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Cosmic Dance: A Comprehensive Guide to the Aurora Borealis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!

