Understanding the Vital Role of Space Weather Prediction Centers
Related Articles: Understanding the Vital Role of Space Weather Prediction Centers
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Vital Role of Space Weather Prediction Centers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Vital Role of Space Weather Prediction Centers

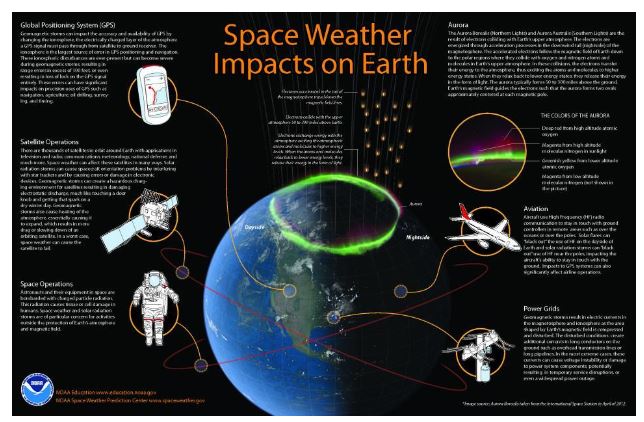
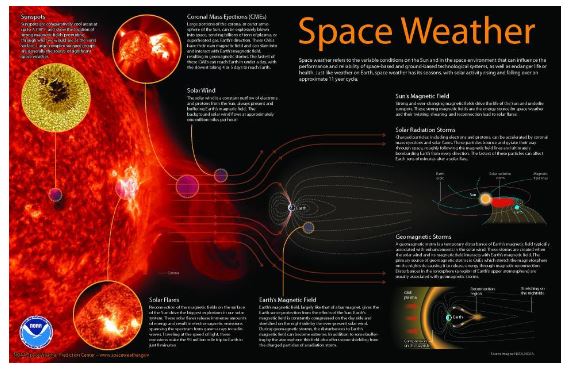
The sun, our life-giving star, is also a powerful force capable of unleashing bursts of energy and particles that can disrupt our technological infrastructure and endanger astronauts in space. These events, collectively known as space weather, can have significant impacts on Earth and its inhabitants. To mitigate these risks, space weather prediction centers play a crucial role in monitoring the sun and forecasting the potential impacts of space weather events.
What is Space Weather?
Space weather refers to the dynamic conditions in the space environment surrounding Earth, primarily driven by the sun’s activity. These conditions can range from relatively benign to extremely disruptive, impacting various technologies and systems we rely upon.
Key Components of Space Weather:
- Solar Flares: Sudden, intense bursts of energy from the sun’s surface, releasing radiation that can disrupt radio communications and harm satellites.
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): Large clouds of magnetized plasma ejected from the sun’s corona, traveling at high speeds and potentially impacting Earth’s magnetic field.
- Solar Energetic Particles (SEPs): High-energy particles accelerated by solar flares and CMEs, posing radiation hazards to astronauts and satellites.
- Geomagnetic Storms: Disturbances in Earth’s magnetic field caused by CMEs or other solar activity, leading to disruptions in power grids, satellite navigation, and radio communications.
The Importance of Space Weather Prediction Centers:
Space weather prediction centers are specialized institutions dedicated to monitoring the sun, analyzing its activity, and forecasting the potential impacts of space weather events on Earth. Their primary goals include:
- Early Warning: Providing timely alerts to critical infrastructure operators, allowing them to take necessary precautions to mitigate potential disruptions.
- Mitigation Strategies: Developing and disseminating strategies to minimize the impacts of space weather events, such as adjusting satellite operations or protecting power grids.
- Research and Development: Conducting research to improve space weather prediction models and develop new technologies for mitigating space weather hazards.
Functions of Space Weather Prediction Centers:
These centers employ a diverse range of tools and techniques to monitor and predict space weather events:
- Space-Based Observatories: Satellites equipped with instruments to observe the sun’s activity, including solar flares, CMEs, and SEPs.
- Ground-Based Observatories: Telescopes and radio antennas to monitor the sun and Earth’s magnetic field, providing data on solar activity and geomagnetic storms.
- Computer Modeling: Sophisticated models to predict the evolution of space weather events and their potential impacts on Earth.
- Data Analysis: Teams of scientists analyze data from various sources to understand the current space weather conditions and forecast future events.
Benefits of Space Weather Prediction Centers:
- Protection of Critical Infrastructure: By providing early warnings and mitigation strategies, space weather prediction centers help protect vital infrastructure, such as power grids, communication networks, and navigation systems.
- Ensuring Space Safety: Early warnings of radiation hazards allow for timely adjustments to spacecraft operations and astronaut activities, safeguarding their safety.
- Scientific Advancement: Research conducted at these centers contributes to a deeper understanding of the sun and its impacts on Earth, advancing our knowledge of space weather phenomena.
Examples of Space Weather Prediction Centers:
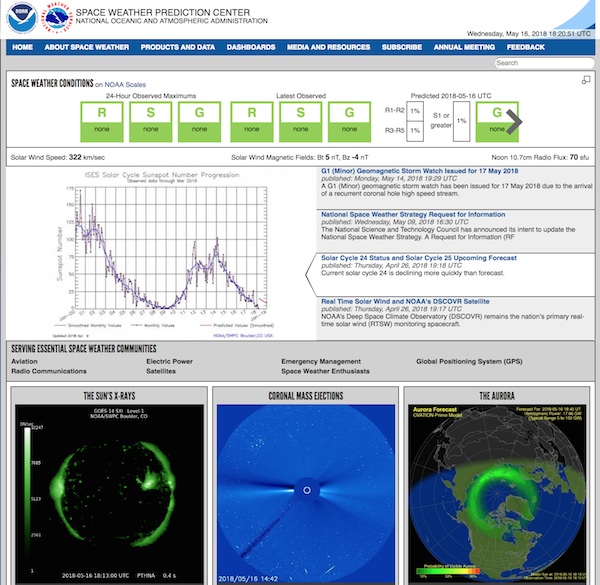
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC): The primary source of space weather information and forecasts in the United States.
- European Space Agency (ESA) Space Weather Service Network: A network of European institutions providing space weather data and forecasts.
- Met Office Space Weather Operations Center: The United Kingdom’s national space weather forecasting center.
Related Searches and FAQs:
1. Space Weather Effects on Satellites:
-
Q: How can space weather affect satellites?
A: Space weather events can cause various issues for satellites, including:
- Radiation damage: Solar flares and SEPs can damage sensitive electronics onboard satellites.
- Atmospheric drag: Geomagnetic storms can cause the Earth’s atmosphere to expand, increasing drag on satellites and affecting their orbits.
- Communication disruptions: Solar flares and geomagnetic storms can disrupt radio communications, impacting satellite operations.
-
Q: What measures are taken to protect satellites from space weather?
A: Several measures are employed to mitigate space weather impacts on satellites:
- Shielding: Satellites are designed with radiation shielding to protect sensitive electronics.
- Orbit adjustments: Satellites can be moved to higher orbits to minimize exposure to radiation.
- Redundant systems: Backup systems are implemented to ensure continued operation in case of failures.
2. Space Weather Effects on Power Grids:
-
Q: How can space weather affect power grids?
A: Geomagnetic storms can induce powerful currents in power grids, leading to:
- Voltage fluctuations: Fluctuations in voltage can damage transformers and other equipment.
- Blackouts: Extreme geomagnetic storms can cause widespread power outages.
-
Q: What measures are taken to protect power grids from space weather?
A: Power grids are becoming more resilient to space weather through:
- Early warning systems: To allow for proactive measures to mitigate impacts.
- Enhanced grid design: Incorporating features to reduce vulnerability to geomagnetically induced currents.
- Increased grid flexibility: Implementing systems to manage voltage fluctuations and prevent blackouts.
3. Space Weather Effects on Radio Communications:
-
Q: How can space weather affect radio communications?
A: Solar flares and geomagnetic storms can disrupt radio communications by:
- Ionospheric disturbances: These events can cause changes in the ionosphere, affecting radio wave propagation.
- Radio blackouts: Intense solar flares can cause radio blackouts, disrupting communication systems.
-
Q: What measures are taken to mitigate space weather impacts on radio communications?
A: Measures include:
- Frequency switching: Using alternative frequencies that are less affected by space weather events.
- Redundant systems: Implementing backup communication systems to ensure continued connectivity.
- Improved forecasting: Accurate space weather forecasts allow for proactive adjustments to communication systems.
4. Space Weather Effects on Navigation Systems:
-
Q: How can space weather affect navigation systems?
A: Geomagnetic storms can disrupt navigation systems by:
- Ionospheric disturbances: These events can affect the accuracy of GPS signals.
- Satellite outages: Geomagnetic storms can cause satellite outages, impacting navigation systems.
-
Q: What measures are taken to mitigate space weather impacts on navigation systems?
A: Measures include:
- Redundant systems: Implementing backup navigation systems to ensure continued operation.
- Improved forecasting: Accurate space weather forecasts allow for adjustments to navigation systems to minimize disruptions.
- Advanced algorithms: Developing algorithms to compensate for ionospheric disturbances and improve accuracy.
5. Space Weather Effects on Aviation:
-
Q: How can space weather affect aviation?
A: Space weather events can impact aviation by:
- Radiation exposure: High-altitude flights can expose passengers and crew to increased radiation levels during solar flares.
- Communication disruptions: Solar flares and geomagnetic storms can disrupt radio communications, impacting air traffic control systems.
- Navigation issues: Geomagnetic storms can disrupt navigation systems, affecting flight paths.
-
Q: What measures are taken to mitigate space weather impacts on aviation?
A: Measures include:
- Flight route adjustments: Airlines can adjust flight paths to minimize exposure to radiation and avoid areas with potential communication disruptions.
- Improved forecasting: Accurate space weather forecasts allow for proactive adjustments to flight plans.
- Radiation monitoring: Aircraft are equipped with radiation detectors to monitor exposure levels.
6. Space Weather Effects on Astronauts:
-
Q: How can space weather affect astronauts?
A: Astronauts are particularly vulnerable to space weather events due to their extended exposure to radiation:
- Radiation exposure: Solar flares and SEPs can expose astronauts to high doses of radiation, increasing the risk of cancer and other health issues.
- Spacewalk risks: Astronauts on spacewalks are especially vulnerable to radiation during solar events.
-
Q: What measures are taken to protect astronauts from space weather?
A: Measures include:
- Spacecraft shielding: Spacecraft are designed with radiation shielding to protect astronauts.
- Radiation monitoring: Astronauts are equipped with dosimeters to monitor radiation exposure levels.
- Mission planning: Spacewalks and other activities are planned to minimize exposure to radiation during solar events.
7. Space Weather Effects on the Aurora Borealis:
-
Q: How does space weather affect the Aurora Borealis?
A: Geomagnetic storms are responsible for the spectacular displays of the Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) and Aurora Australis (Southern Lights).
-
Q: What are the conditions that create the Aurora Borealis?
A: When charged particles from the sun interact with Earth’s magnetic field, they are channeled towards the poles, where they collide with atoms in the atmosphere, causing them to emit light, creating the aurora.
8. Space Weather Effects on Climate Change:
-
Q: How does space weather affect climate change?
A: While space weather events have a negligible impact on long-term climate change, they can influence short-term weather patterns.
-
Q: What are the potential effects of space weather on climate?
A: Geomagnetic storms can affect atmospheric circulation, leading to localized temperature fluctuations and precipitation changes. However, these effects are generally short-lived and do not contribute significantly to long-term climate change.
Tips for Mitigating Space Weather Impacts:
- Stay informed: Monitor space weather forecasts from reliable sources, such as the NOAA SWPC.
- Prepare for disruptions: Develop contingency plans for potential disruptions to critical infrastructure, communication systems, and navigation.
- Invest in resilience: Enhance the resilience of infrastructure by implementing protective measures against space weather hazards.
- Support research: Encourage and support research to improve space weather prediction capabilities and mitigation strategies.
Conclusion:
Space weather prediction centers are essential for safeguarding our technological infrastructure, ensuring the safety of astronauts, and advancing our understanding of the sun and its impacts on Earth. By monitoring solar activity, analyzing data, and forecasting potential impacts, these centers provide early warnings and mitigation strategies, enabling us to prepare for and minimize the disruptions caused by space weather events. As our reliance on technology continues to grow, the importance of space weather prediction centers will only increase, ensuring the resilience of our society to this powerful force from the sun.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Vital Role of Space Weather Prediction Centers. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!