Understanding the Kp Index: A Guide to Geomagnetic Activity
Related Articles: Understanding the Kp Index: A Guide to Geomagnetic Activity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Kp Index: A Guide to Geomagnetic Activity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Kp Index: A Guide to Geomagnetic Activity

The Kp index, a cornerstone of space weather forecasting, provides a crucial measure of geomagnetic activity. This index, which stands for "planetarische Kennziffer" (German for "planetary character figure"), quantifies the strength of disturbances in the Earth’s magnetic field caused by solar activity. These disturbances, known as geomagnetic storms, can have far-reaching consequences, impacting everything from satellite operations to power grids and even influencing auroral displays.
What Causes Geomagnetic Storms?
Solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are the primary drivers of geomagnetic storms. Solar flares are intense bursts of energy from the Sun’s surface, releasing vast amounts of radiation. CMEs, on the other hand, are massive eruptions of plasma and magnetic field lines that travel outward from the Sun.
When these solar events occur, they can release a significant amount of charged particles that interact with the Earth’s magnetic field. This interaction causes the field to become distorted, leading to geomagnetic storms.
The Kp Index: A Scaled Measurement
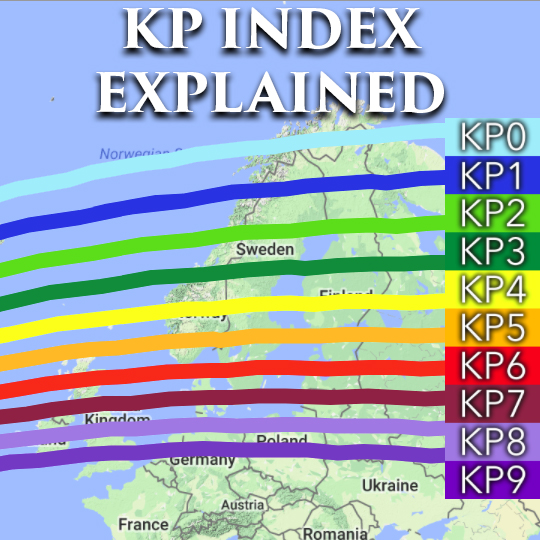
The Kp index is a three-hour average of the maximum deviation in the Earth’s horizontal magnetic field component. It is a scaled measurement, ranging from 0 to 9, with higher values indicating stronger geomagnetic activity.
- Kp 0-3: Quiet geomagnetic conditions, typical of normal days.
- Kp 4-5: Minor geomagnetic storms, potentially impacting some technological systems.
- Kp 6-7: Moderate geomagnetic storms, causing noticeable disruptions to satellite operations and power grids.
- Kp 8-9: Strong to severe geomagnetic storms, leading to widespread disruptions and potentially triggering auroras at lower latitudes.
The Importance of Monitoring Kp
Understanding and monitoring the Kp index is vital for various reasons:
- Satellite Operations: Geomagnetic storms can disrupt satellite communications, navigation systems, and even damage sensitive instruments.
- Power Grids: Strong geomagnetic storms can induce currents in power lines, potentially leading to blackouts.
- Aviation: High-latitude flights can be affected by geomagnetic storms, impacting navigation systems and increasing radiation exposure for passengers and crew.
- Auroral Displays: Geomagnetic storms are responsible for the spectacular auroral displays, often visible in high-latitude regions.
- Space Weather Forecasting: The Kp index is a critical tool for space weather forecasting, allowing scientists to predict and prepare for potential geomagnetic storms.
Beyond the Kp Index: Additional Measures of Geomagnetic Activity
While the Kp index provides a valuable overview of geomagnetic activity, other metrics offer more detailed information:
- Dst Index: Measures the strength of the geomagnetic field at the equator.
- Ap Index: A daily average of the Kp index, providing a broader picture of geomagnetic activity over a 24-hour period.
- Solar Wind Parameters: These include measurements of the solar wind’s speed, density, and magnetic field strength, which can provide insights into the potential for geomagnetic storms.
Related Searches:
Here are some related searches that provide further insights into geomagnetic activity and the Kp index:
- Geomagnetic Storm Effects: Understanding the impact of geomagnetic storms on various systems and technologies.
- Space Weather Forecast: Accessing real-time and predicted space weather information, including Kp index values.
- Aurora Borealis: Exploring the science behind auroral displays and their relationship to geomagnetic activity.
- Solar Flares and CMEs: Learning about these solar events and their role in driving geomagnetic storms.
- Solar Cycle: Understanding the cyclical nature of solar activity and its influence on geomagnetic storms.
- Geomagnetic Activity Levels: Exploring the different levels of geomagnetic activity and their corresponding effects.
- Space Weather Impacts: Examining the potential consequences of geomagnetic storms on various aspects of our lives.
- Geomagnetic Storm Prediction: Understanding the methods and tools used to predict geomagnetic storms.
FAQs about Kp Index:
-
Q: What is the relationship between Kp index and auroras?
- A: Higher Kp values indicate stronger geomagnetic activity, which increases the likelihood and intensity of auroral displays.
-
Q: How often do geomagnetic storms occur?
- A: Geomagnetic storms can occur frequently, but their intensity varies significantly. Minor storms are relatively common, while severe storms are less frequent.
-
Q: Can I see auroras if the Kp index is low?
- A: While auroras are more likely during periods of high Kp values, they can sometimes be observed even during periods of low activity, especially in high-latitude regions.
-
Q: How can I stay informed about the Kp index?
- A: Various organizations, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC), provide real-time and predicted Kp index values.
-
Q: What can I do to prepare for a geomagnetic storm?
- A: While most geomagnetic storms have minimal impact on daily life, it’s essential to stay informed about potential disruptions and follow any guidelines issued by authorities.
Tips for Understanding and Using Kp Index:
- Check Space Weather Forecasts: Regularly monitor space weather forecasts from reputable sources like NOAA and SWPC.
- Understand the Impact of Geomagnetic Storms: Familiarize yourself with the potential consequences of geomagnetic storms on various systems and technologies.
- Take Precautions During High Kp Events: If a high Kp event is predicted, consider taking precautions such as avoiding sensitive electronics and high-latitude flights.
- Share Information: Spread awareness about the Kp index and the importance of space weather forecasting.
Conclusion:
The Kp index is a valuable tool for understanding and predicting geomagnetic activity. By monitoring this index, we can gain insights into the potential impact of solar events on our technological infrastructure and prepare for potential disruptions. It is essential to stay informed about space weather and the Kp index to ensure the safety and functionality of our critical systems and to appreciate the wonders of our dynamic solar system.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Kp Index: A Guide to Geomagnetic Activity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!

