Argentina and Venezuela: A Comparative Study of Two South American Nations
Related Articles: Argentina and Venezuela: A Comparative Study of Two South American Nations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Argentina and Venezuela: A Comparative Study of Two South American Nations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Argentina and Venezuela: A Comparative Study of Two South American Nations

This article provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of Argentina and Venezuela, two prominent South American nations with distinct histories, cultures, and economic trajectories. The analysis delves into their political systems, economic landscapes, social structures, and cultural expressions, highlighting key similarities and differences.
Historical Context:
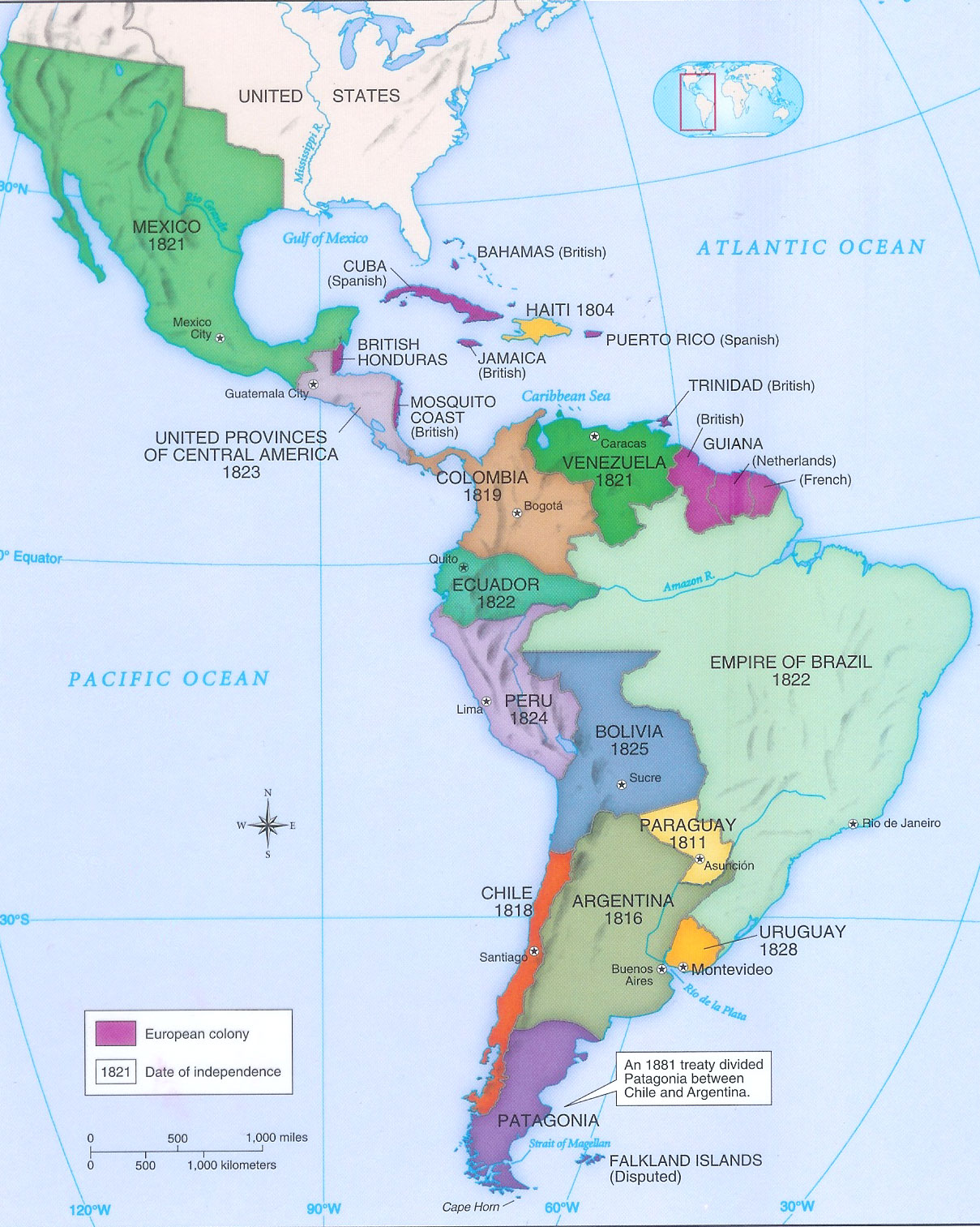
Argentina: Argentina’s history is marked by a complex interplay of European influence, indigenous cultures, and internal political struggles. After gaining independence from Spain in 1816, Argentina experienced periods of political instability, economic booms, and social reforms. The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed significant economic growth fueled by agricultural exports and European immigration. However, Argentina’s economic prosperity was often marred by social inequalities and political turmoil. The 20th century saw Argentina grapple with military dictatorships, economic crises, and political polarization.
Venezuela: Venezuela’s history is closely intertwined with the discovery of oil in the early 20th century. Oil exports propelled Venezuela to economic prosperity, transforming the country from a predominantly agricultural society to a major oil producer. However, Venezuela’s dependence on oil also created vulnerabilities, leading to economic fluctuations and political instability. The country experienced a period of democratic governance in the 1950s and 1960s, followed by a period of military rule in the 1970s. The late 20th century witnessed the rise of Hugo Chávez, a charismatic leader who implemented socialist policies and centralized power.
Political Systems:
Argentina: Argentina is a federal republic with a multi-party system. The country’s political system is characterized by a strong executive branch, a bicameral legislature, and an independent judiciary. Argentina has a long tradition of democratic governance, although it has also experienced periods of military rule. The country’s political landscape is often characterized by ideological divisions, with the Peronist movement, founded by former President Juan Perón, playing a significant role in Argentine politics.
Venezuela: Venezuela’s political system has undergone significant transformations in recent decades. Following a period of democratic governance, Venezuela experienced a shift towards a socialist model under Hugo Chávez, who came to power in 1999. Chávez’s policies centralized power in the executive branch, weakened democratic institutions, and suppressed opposition. His successor, Nicolás Maduro, continued to implement socialist policies, leading to an economic crisis and a decline in democratic freedoms.
Economic Landscapes:
Argentina: Argentina’s economy has historically been characterized by fluctuations, with periods of economic growth often followed by recessions. The country’s economic performance has been influenced by factors such as agricultural exports, industrial production, and government policies. Argentina has a diversified economy, with significant contributions from agriculture, industry, and services. However, the country has faced challenges such as high inflation, public debt, and economic instability.
Venezuela: Venezuela’s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports. The country holds the world’s largest proven oil reserves, but its dependence on oil has created vulnerabilities. Declining oil prices, government mismanagement, and corruption have led to an economic crisis, characterized by hyperinflation, shortages of essential goods, and a decline in living standards.
Social Structures:
Argentina: Argentina has a diverse population, with a significant European heritage. The country has a strong middle class, but social inequalities persist. Argentina has a robust social welfare system, providing healthcare, education, and social security benefits to its citizens. However, the country faces challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and income inequality.
Venezuela: Venezuela’s social structure has been significantly impacted by the country’s economic crisis. The once-strong middle class has been decimated, and poverty rates have soared. The government’s socialist policies have resulted in shortages of basic necessities, including food, medicine, and electricity. Venezuela’s social fabric has been strained by political polarization, social unrest, and a decline in public services.
Cultural Expressions:
Argentina: Argentina is renowned for its vibrant culture, characterized by its passionate tango music and dance, its rich literary tradition, and its distinctive cuisine. Argentina has a strong national identity, shaped by its history, its European heritage, and its diverse cultural influences. The country is also known for its sporting prowess, particularly in football (soccer).
Venezuela: Venezuela’s culture is a blend of indigenous, African, and European influences. The country is known for its lively music, including salsa, merengue, and joropo. Venezuela also has a rich artistic heritage, with a vibrant tradition of painting, sculpture, and literature. The country’s culture is deeply rooted in its oil wealth and its history of political and social transformations.
Related Searches:
1. Argentina Economy:
- Economic History: Explore Argentina’s economic history, focusing on periods of growth and decline, key economic policies, and the impact of global events.
- Key Industries: Analyze Argentina’s major industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and services, highlighting their contributions to the economy and employment.
- Economic Challenges: Discuss Argentina’s economic challenges, such as inflation, public debt, and economic instability, and explore potential solutions.
- Economic Outlook: Analyze Argentina’s economic outlook, considering current trends, government policies, and potential risks and opportunities.
2. Venezuela Economy:
- Oil Dependence: Examine the role of oil in Venezuela’s economy, its impact on economic growth and vulnerability, and the implications of declining oil prices.
- Economic Crisis: Analyze the causes and consequences of Venezuela’s economic crisis, including hyperinflation, shortages, and declining living standards.
- Social Impact: Discuss the social impact of Venezuela’s economic crisis, including rising poverty, unemployment, and social unrest.
- Economic Recovery: Explore potential strategies for Venezuela’s economic recovery, considering factors such as political stability, institutional reforms, and diversification of the economy.
3. Argentina Politics:
- Political System: Analyze Argentina’s political system, including the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and the role of political parties.
- Historical Overview: Provide a historical overview of Argentina’s political system, including periods of democracy, military rule, and political instability.
- Current Political Landscape: Discuss the current political landscape in Argentina, including key political parties, ideologies, and political challenges.
- International Relations: Examine Argentina’s role in international affairs, its relationships with other countries, and its involvement in regional and global organizations.
4. Venezuela Politics:
- Chavismo: Analyze the impact of Hugo Chávez’s socialist policies on Venezuela’s political system, including the centralization of power, the weakening of democratic institutions, and the suppression of opposition.
- Political Crisis: Discuss the political crisis in Venezuela, including the erosion of democratic freedoms, human rights violations, and the legitimacy of the Maduro government.
- International Sanctions: Examine the impact of international sanctions on Venezuela’s economy and political system, and their implications for the country’s future.
- Political Transition: Explore potential scenarios for a political transition in Venezuela, including the role of international actors, the possibility of elections, and the prospects for democratic restoration.
5. Argentina Culture:
- Tango: Explore the history, evolution, and cultural significance of tango music and dance in Argentina.
- Literature: Discuss Argentina’s rich literary tradition, highlighting prominent authors, literary movements, and key works.
- Cuisine: Analyze Argentina’s distinctive cuisine, focusing on traditional dishes, culinary influences, and the role of food in Argentine culture.
- Sports: Examine the importance of sports in Argentine culture, focusing on football (soccer), rugby, and other popular sports.
6. Venezuela Culture:
- Music: Explore the diverse musical genres of Venezuela, including salsa, merengue, joropo, and traditional indigenous music.
- Art: Discuss Venezuela’s artistic heritage, highlighting prominent painters, sculptors, and literary figures.
- Cultural Influences: Analyze the various cultural influences that have shaped Venezuela’s culture, including indigenous, African, and European traditions.
- Social Customs: Examine social customs and traditions in Venezuela, including family structures, social etiquette, and cultural values.
7. Argentina vs. Venezuela Comparison:
- Political Systems: Compare and contrast the political systems of Argentina and Venezuela, highlighting key similarities and differences.
- Economic Performance: Analyze the economic performance of Argentina and Venezuela, comparing their economic structures, growth patterns, and challenges.
- Social Development: Compare and contrast the social structures and development indicators of Argentina and Venezuela, focusing on poverty rates, income inequality, and access to public services.
- Cultural Expressions: Compare and contrast the cultural expressions of Argentina and Venezuela, highlighting their distinct artistic traditions, music, and social customs.
8. Argentina and Venezuela: A Historical Perspective:
- Colonial Legacy: Examine the impact of the Spanish colonial legacy on both Argentina and Venezuela, including cultural influences, social structures, and political systems.
- Independence Movements: Compare and contrast the independence movements in Argentina and Venezuela, highlighting key figures, strategies, and outcomes.
- 20th Century Developments: Analyze the major political and economic developments in Argentina and Venezuela during the 20th century, including periods of economic growth, political instability, and social change.
- Contemporary Challenges: Discuss the contemporary challenges facing both Argentina and Venezuela, including economic crises, political polarization, and social unrest.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main similarities between Argentina and Venezuela?
A: Both Argentina and Venezuela are large, diverse countries in South America with a rich history and culture. They share a common colonial past under Spanish rule, and both have experienced periods of economic prosperity and political instability. Both countries have a strong national identity and a passion for football (soccer).
Q: What are the main differences between Argentina and Venezuela?
A: Argentina has a more diversified economy, with a greater focus on agriculture and industry, while Venezuela’s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports. Argentina has a longer tradition of democratic governance, while Venezuela has experienced a shift towards a socialist model under Hugo Chávez and his successor, Nicolás Maduro. Argentina has a stronger middle class and a more robust social welfare system, while Venezuela has experienced a decline in living standards and a widening gap between rich and poor.
Q: What are the main challenges facing Argentina?
A: Argentina faces challenges such as high inflation, public debt, economic instability, and political polarization. The country’s economic performance has been volatile, with periods of growth often followed by recessions. Argentina also faces social challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and income inequality.
Q: What are the main challenges facing Venezuela?
A: Venezuela faces an unprecedented economic crisis, characterized by hyperinflation, shortages of essential goods, and a decline in living standards. The country’s political system has become increasingly authoritarian, with the Maduro government suppressing opposition and restricting democratic freedoms. Venezuela also faces social challenges, including rising poverty, unemployment, and social unrest.
Q: What are the prospects for the future of Argentina and Venezuela?
A: The future of both Argentina and Venezuela is uncertain. Argentina has the potential to overcome its economic challenges and achieve sustained growth, but it faces political and social obstacles. Venezuela’s economic crisis is severe, and its political system is deeply polarized. The country’s future will depend on factors such as political stability, economic reforms, and international support.
Tips:
- Engage in informed political discourse: Stay informed about current events and political developments in both Argentina and Venezuela. Engage in respectful discussions with others, listening to diverse perspectives and avoiding generalizations.
- Support democratic values: Advocate for democratic principles, human rights, and the rule of law in both countries. Support organizations that promote democracy, transparency, and accountability.
- Promote economic diversification: Encourage both Argentina and Venezuela to diversify their economies, reducing their dependence on specific industries or commodities. Support initiatives that promote entrepreneurship, innovation, and sustainable development.
- Foster cultural exchange: Encourage cultural exchange between Argentina and Venezuela, promoting understanding, appreciation, and collaboration between their people.
Conclusion:
Argentina and Venezuela are two South American nations with distinct histories, cultures, and economic trajectories. Argentina has a more diversified economy and a longer tradition of democratic governance, while Venezuela’s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports and its political system has become increasingly authoritarian. Both countries face challenges, but they also have the potential to overcome them and achieve a brighter future. By understanding their unique histories, political systems, economic landscapes, and cultural expressions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of these two fascinating nations.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-594463288-fdbac3735cc348b89ee8eca44afd964c.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Argentina and Venezuela: A Comparative Study of Two South American Nations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!

